文本
从 Cypress 测试中调用 GraphQL
把所有的 todos 都取出来
首先,让我们看看我们的 Cypress 测试如何获取所有 todo 项。例如,这允许我们确认应用程序所显示的内容。让我们使用 cy.request 命令获取这些项。
cypress/integration/request-spec.js
it('fetches all items', () => {
cy.request({
method: 'POST',
url: 'http://localhost:3000/',
body: {
operationName: 'allTodos',
query: `
query allTodos {
allTodos {
id,
title,
completed
}
}
`,
},
})
})
提示: 如果您不确定 body 对象,请查看应用程序正在进行的网络调用,并从那里复制 GraphQL 查询。
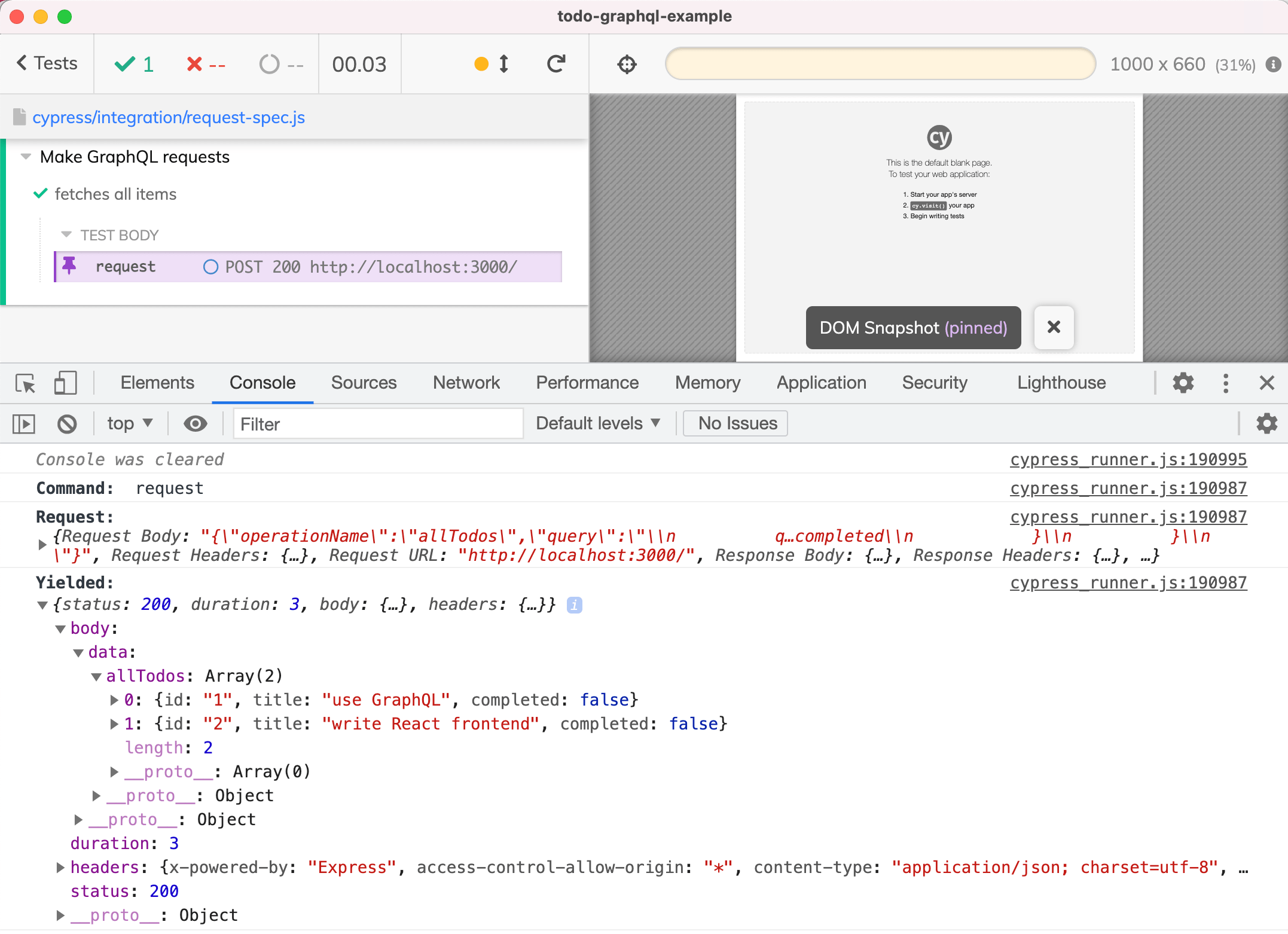 从响应对象中,我们可以得到 todos 列表,并确认它们的数量和其他细节。
从响应对象中,我们可以得到 todos 列表,并确认它们的数量和其他细节。
cy.request({ ... })
.its('body.data.allTodos')
.should('have.length', 2)
注意,如果您不知道项目的精确数量,但是应该在 > = 0的项目使用.Gte 断言
cy.request({ ... })
.its('body.data.allTodos')
.should('have.length.gte', 0)
使用应用程序客户端 与直接使用 cy.request 不同,我们可以使用应用程序使用的同一个 GraphQL 客户端获取项目!只需确保将“ cache”设置为 false,以避免应用程序和测试运行程序客户端的内存缓存之间出现竞争条件。
假设这是一个源文件,其中导出了 GraphQL 客户机
src/graphql-client.js
// imports and init code
export const client = new ApolloClient({
link: concat(operationNameLink, httpLink),
fetchOptions: {
mode: 'no-cors',
},
cache: new InMemoryCache(),
})
然后,我们可以通过从 spec 文件导入 GraphQL 客户机创建一个实例。注意: 这将从应用程序的 GraphQL 客户端实例中创建一个单独的客户端实例。
import { gql } from '@apollo/client'
import { client } from '../../src/graphql-client'
it('fetches all items using application client', () => {
// make a GraphQL query using the app's client
// https://www.apollographql.com/docs/react/data/queries/
const query = gql`
query allTodos {
allTodos {
id
title
completed
}
}
`
// use https://on.cypress.io/wrap to let the Cypress test
// wait for the promise returned by the "client.query" to resolve
cy.wrap(
client.query({
query,
// it is important to AVOID any caching here
// and fetch the current server data
fetchPolicy: 'no-cache',
}),
)
.its('data.allTodos')
.should('have.length', 2)
})
测试通过了
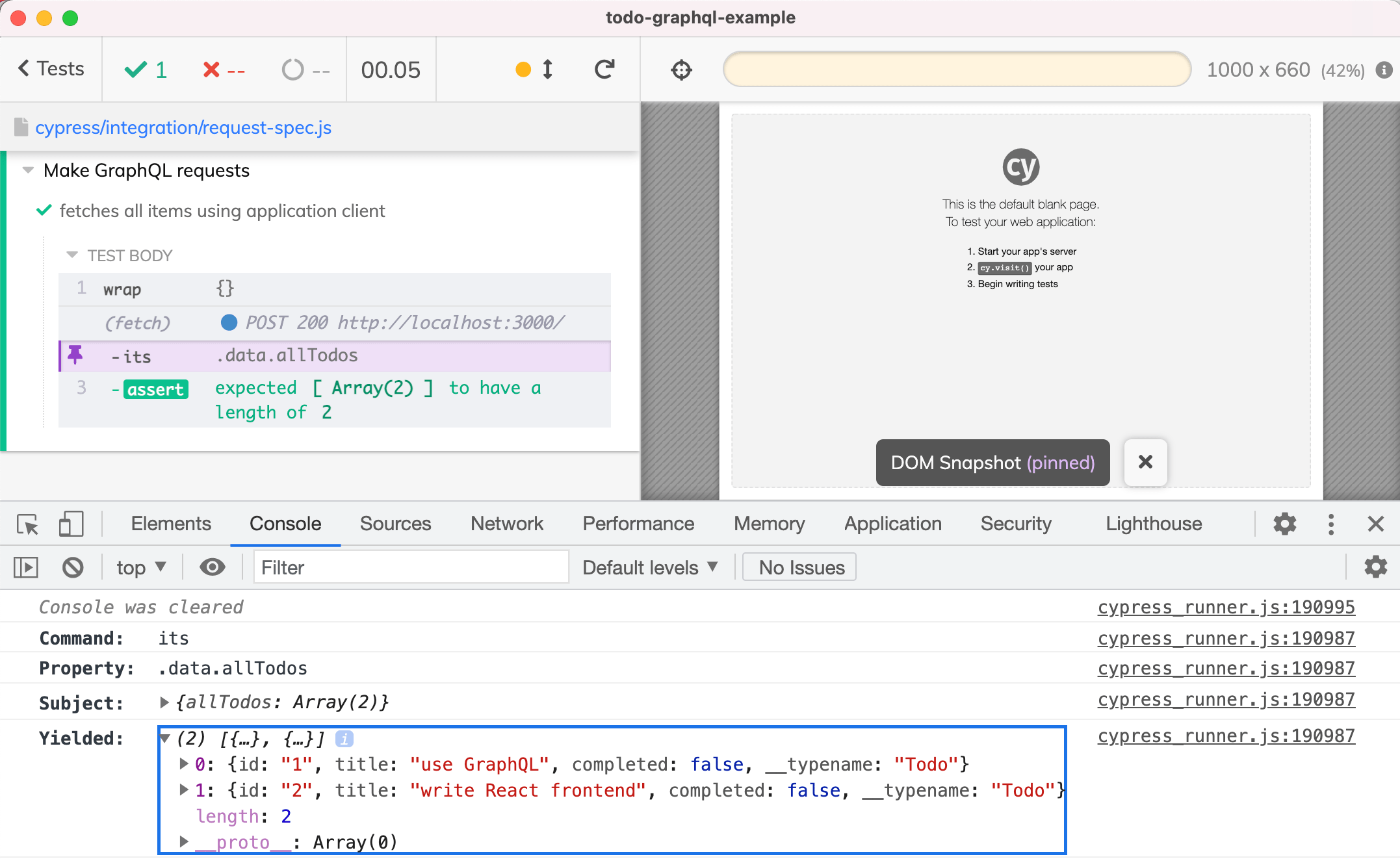
使用加载的 GraphQL 客户机请求待办事项列表
添加项目
使用 GraphQL 客户机,甚至在应用程序和 specs 之间共享查询都非常方便。例如,让我们创建一个条目,然后确认它在应用程序中是可见的。
cypress/integration/request-spec.js
import { gql } from '@apollo/client'
import { client } from '../../src/graphql-client'
it('creates one item', () => {
const random = Cypress._.random(1e5)
const title = `test ${random}`
cy.log(`Adding item ${title}`)
.then(() => {
const query = gql`
mutation AddTodo($title: String!) {
createTodo(title: $title, completed: false) {
id
}
}
`
// by returning the promise returned by the "client.query"
// call from the .then callback, we force the test to wait
// and yield the result to the next Cypress command or assertion
return client.query({
query,
variables: {
title,
},
// it is important to AVOID any caching here
// and fetch the current server data
fetchPolicy: 'no-cache',
})
})
// use zero timeout to avoid "cy.its" retrying
// since the response object is NOT going to change
.its('data.createTodo', { timeout: 0 })
.should('have.property', 'id')
// the item we have created should be shown in the list
cy.visit('/')
cy.contains('.todo', title)
})
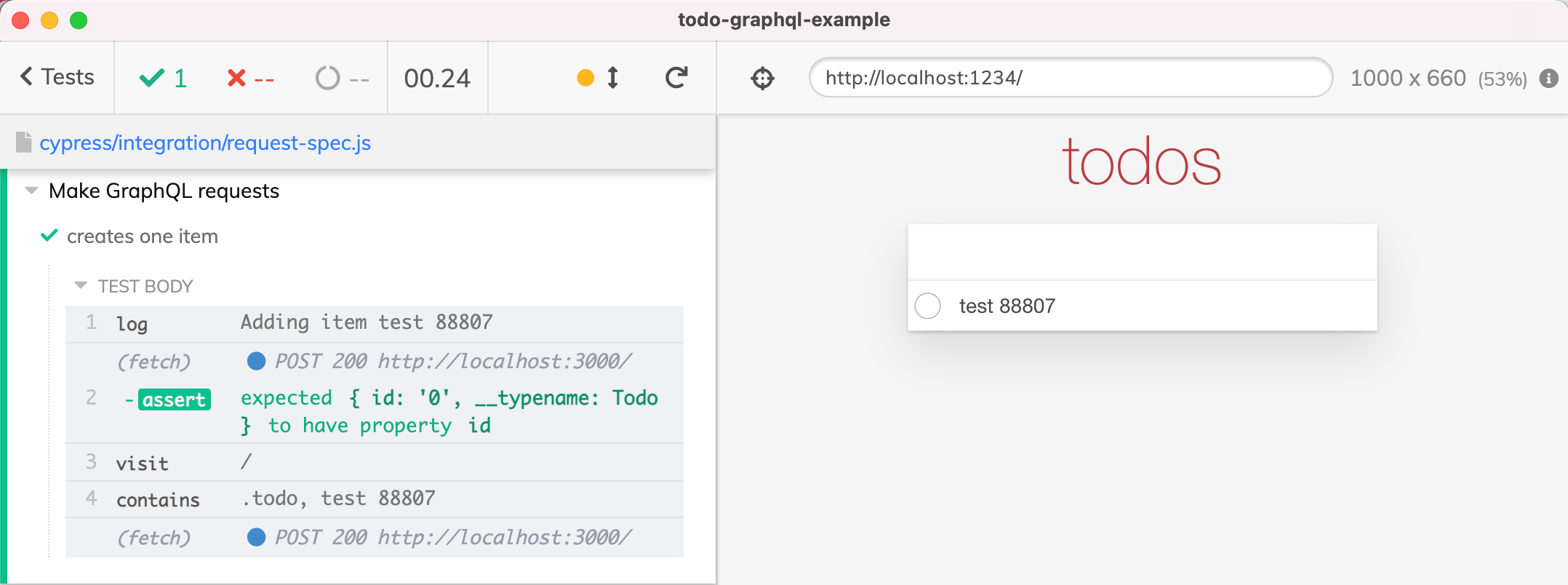 使用 GraphQL 变异创建一个项目
使用 GraphQL 变异创建一个项目
如果 spec 文件从应用程序的源文件导入 GraphQL 客户机,那么它将创建自己的实例,独立于应用程序在 iframe 中创建的 GraphQL 客户机。这有一些优点,例如,上面的测试可以在 cy.visit 命令加载应用程序之前执行 GraphQL 变异。但是如果你想在应用程序和 spec 之间共享 GraphQL 客户端,有一种方法:
export const client = new ApolloClient({
...
}
if (window.Cypress) {
window.graphqlClient = client
}
我们将应用程序创建的客户机引用设置为窗口对象的属性。从规范中,我们可以获取这个属性并使用它来侦查和存根客户机方法调用。下面是一个典型的测试:
访问该页面。应用程序创建一个 GraphQL 客户端对象并将其设置为window.graphqlClient value.
因此,我们可以直接重试,直到我们使用cy.visit('/').should('have.property', 'graphqlClient') assertion. 断言 一旦我们有了对象引用,我们就可以使用cy.spy and 及cy.stub to observe / stub the calls the application is making.
it('adds a todo', () => {
// set up the spy on "client.mutate" method
cy.visit('/')
.should('have.property', 'graphqlClient')
.then((client) => {
cy.spy(client, 'mutate').as('mutate')
})
// have the application make the call by using the UI
cy.get('.new-todo').type('Test!!!!{enter}')
// confirm the call has happened with expected variables
cy.get('@mutate')
.should('have.been.calledOnce')
.its('firstCall.args.0.variables')
.should('deep.include', {
title: 'Test!!!!',
})
.and('have.property', 'id')
})
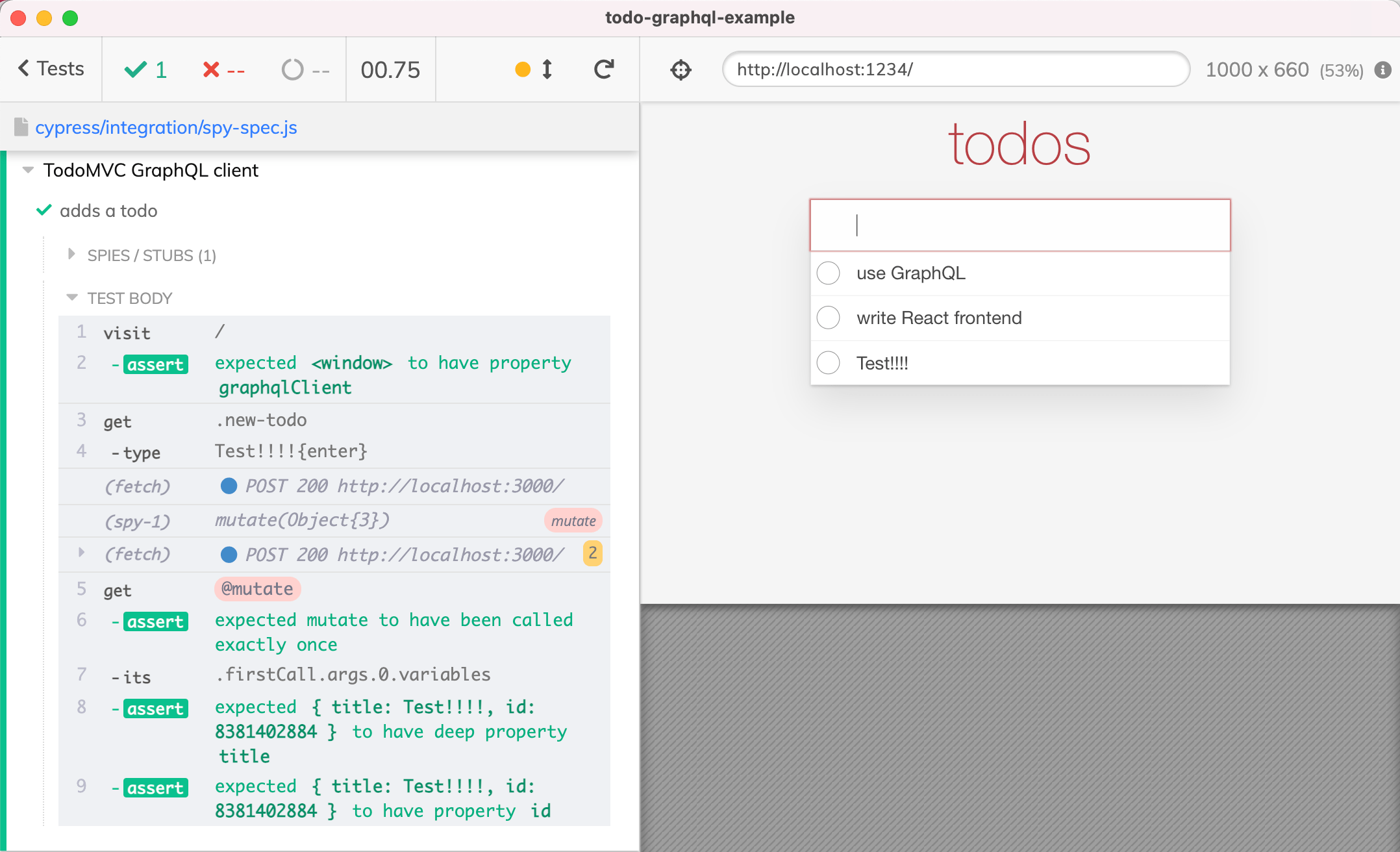
别名 提示: 我们使用 cy.as 命令给了间谍一个化名“ mutate”。后面的“ this [ alias name ]”语法使用测试上下文获取这些别名。因为(名称)命令已经结束。Cypress 强制所有命令逐个运行,因此我们可以使用“ this [ alias name ]”语法从。后面的(function (){ ... })回调函数。作为命令。
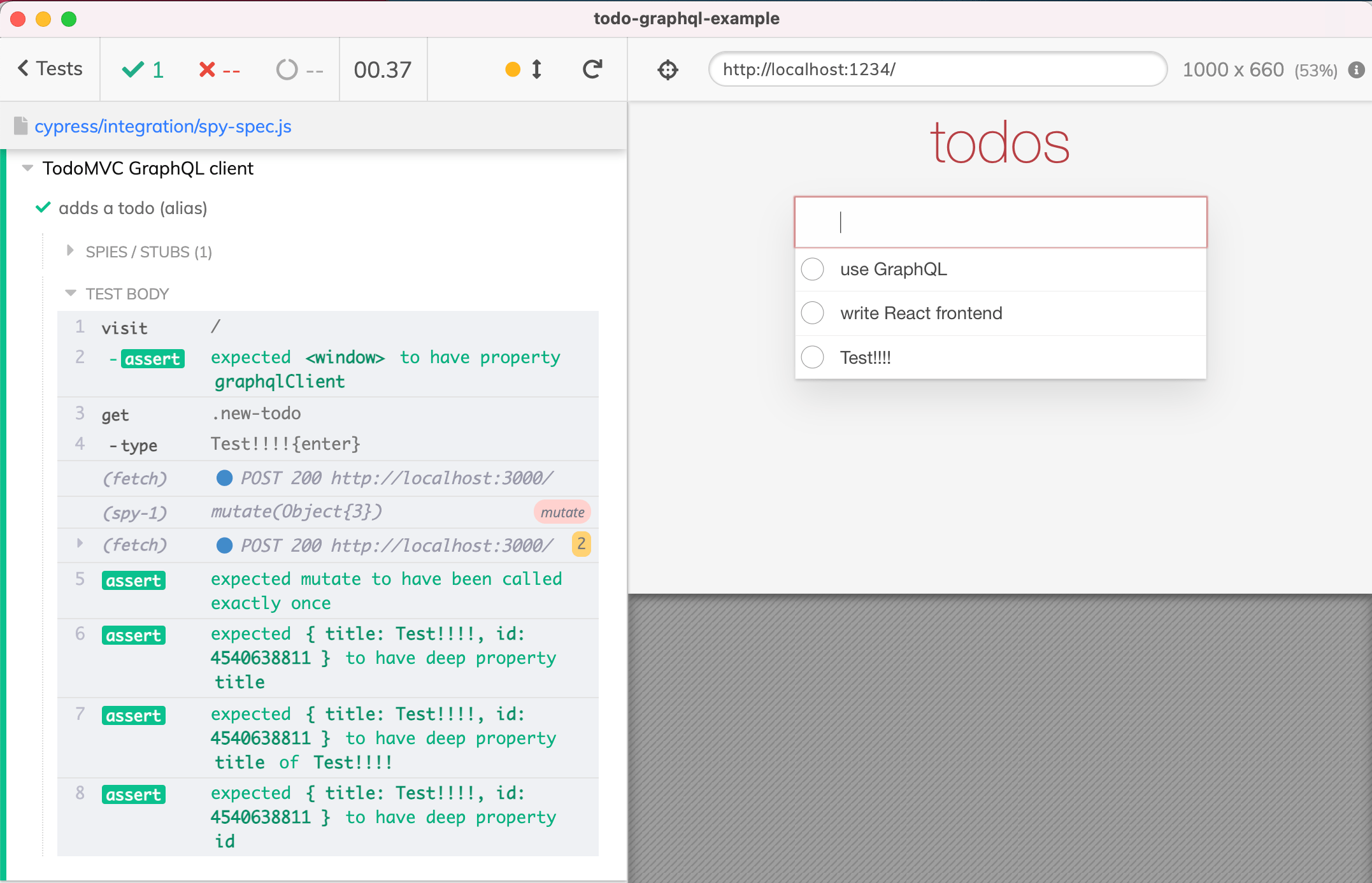
it('adds a todo (alias)', () => { // set up the spy on "client.mutate" method cy.visit('/') .should('have.property', 'graphqlClient') .then((client) => { // once the ".as" command finishes // we can access the spy using the "this.mutate" property cy.spy(client, 'mutate').as('mutate') }) // have the application make the call by using the UI cy.get('.new-todo') .type('Test!!!!{enter}') // note the "function () { ... }" syntax is used to // make sure the "this" points at the test context object .then(function () { // confirm the call has happened with expected variables // by now the client.mutate has been called, // and the alias has been set (no retries for here) expect(this.mutate).to.have.been.calledOnce expect(this.mutate.firstCall.args[0].variables) .to.deep.include({ title: 'Test!!!!', }) .and.to.have.property('id') }) })
由于预期(this.mutate)。不要重试,确保只有在客户端调用确定之后才使用它。
 删除所有待办事项
删除所有待办事项
对于端到端测试,一个非常常见的问题是在测试之前清除现有的数据。假设您有一个 GraphQL 端点,您可以获得所有 Todo 项目?你会怎样删除它们呢?如果你没有变异“删除所有的 x”,那么你需要一个一个地删除每个项目。
下面是如何做到这一点: 首先,让我们编写一个可重用的方法,并将其放在 utils.js 文件中。
import { gql } from '@apollo/client'
import { client } from '../../src/graphql-client'
export function deleteAll() {
// fetches all todo items, grabs their IDs, and deletes them
cy.log('**deleteAll**')
.then(() =>
client.query({
// it is important to AVOID any caching here
// and fetch the current server data
fetchPolicy: 'no-cache',
query: gql`
query getAllTodos {
allTodos {
id
}
}
`,
}),
)
.its('data.allTodos')
// from each item, grab just the property "id"
.then((items) => Cypress._.map(items, 'id'))
.then((ids) => {
if (!ids.length) {
cy.log('Nothing to delete')
return
}
cy.log(`Found **${ids.length}** todos`)
// delete all items one by one
ids.forEach((id) => {
const mutation = gql`
mutation deleteTodo {
removeTodo(id: "${id}") {
id
}
}
`
cy.log(`deleting item id:**${id}**`).then(
() =>
client.mutate({
mutation,
}),
{ log: false },
)
})
})
}
我们可以在每次测试之前或者任何时候使用这个方法:
import { deleteAll } from './utils'
describe('Delete items', () => {
beforeEach(deleteAll)
it('deletes all items by making GraphQL calls', () => {
cy.intercept({
method: 'POST',
url: '/',
headers: {
'x-gql-operation-name': 'allTodos',
},
}).as('allTodos')
cy.visit('/')
cy.wait('@allTodos').its('response.body.data.allTodos').should('be.empty')
cy.get('.todo').should('have.length', 0)
})
})
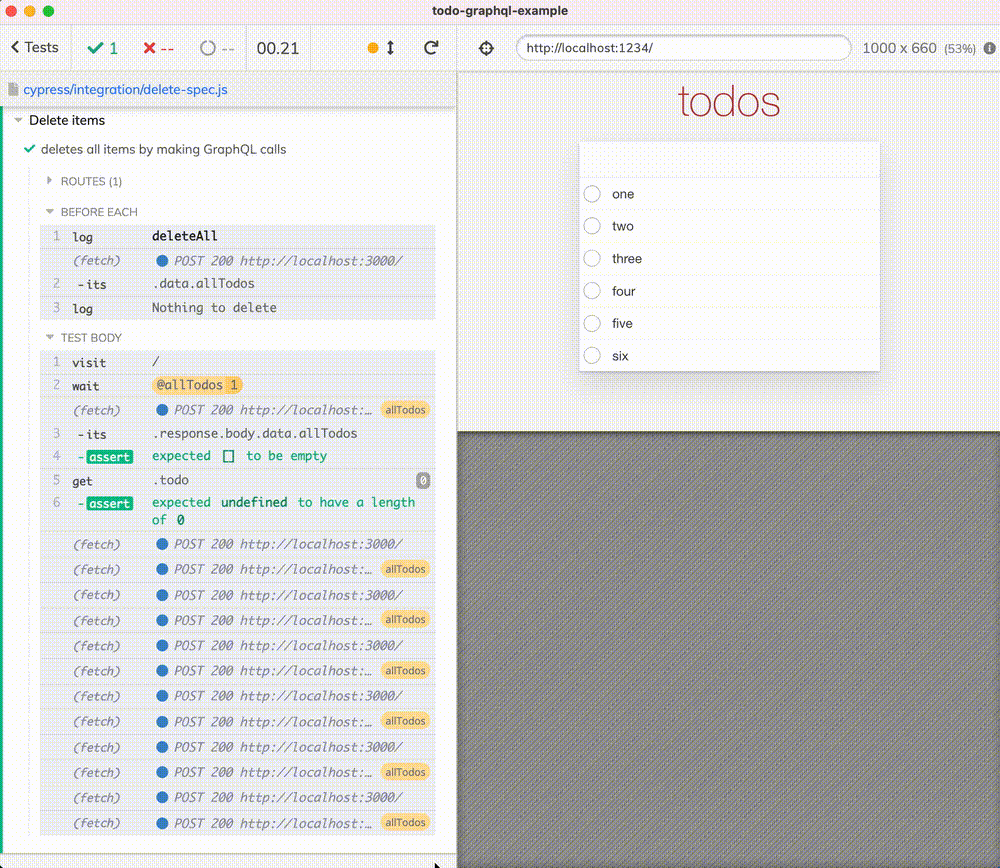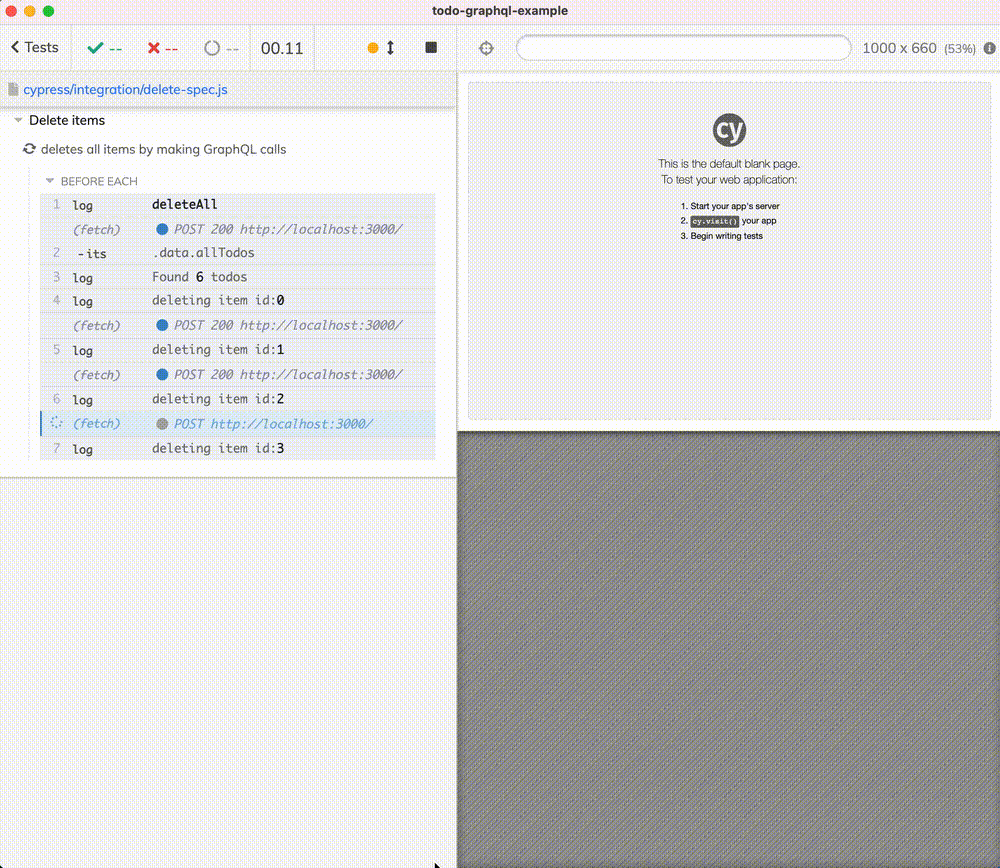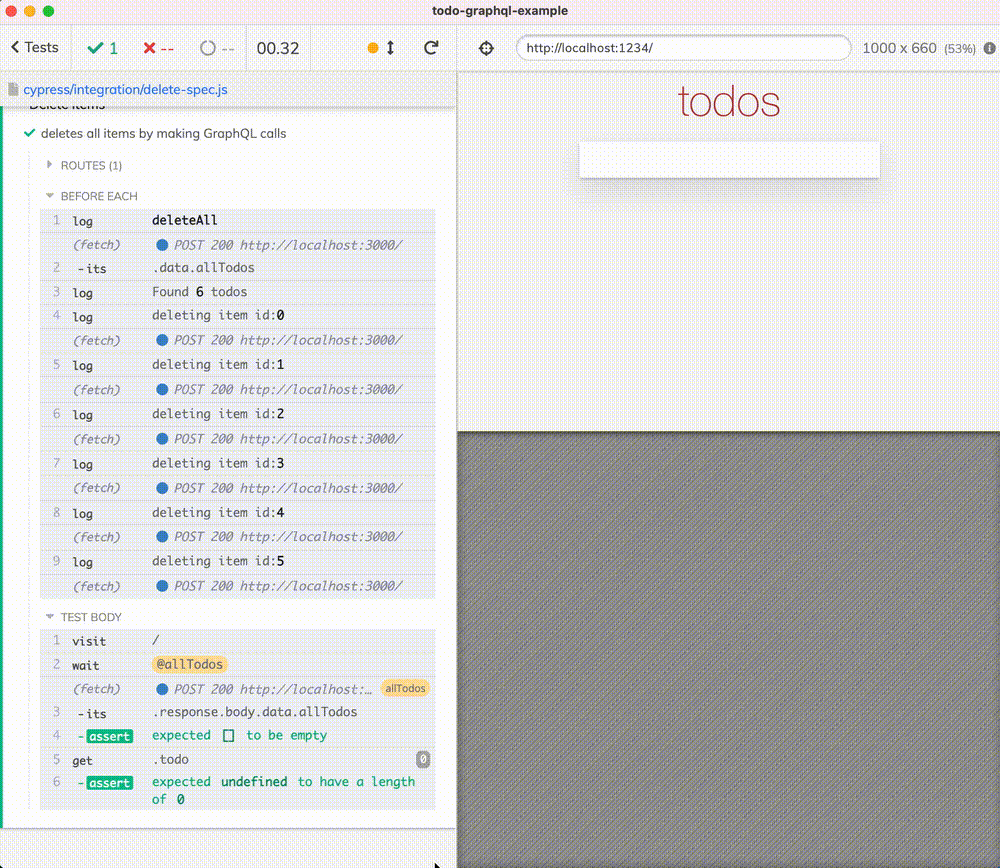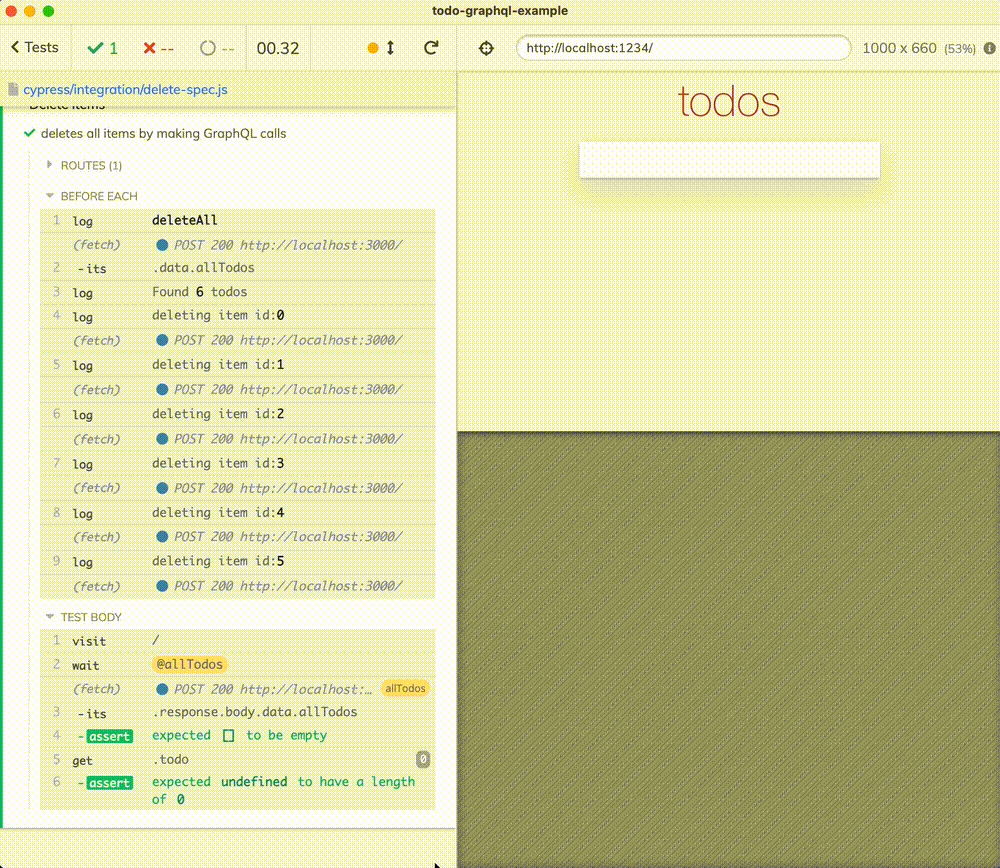 逐一删除每个项目
逐一删除每个项目
您可以在下面的视频中看到使用 GraphQL 调用删除所有项目
https://youtu.be/l7E7K7x7V8g
author
石头 磊哥 seven 随便叫
company
HSBC 大家好,我已经加入了HSBC
roles
QA(营生) dev(front-end dev 兴趣爱好)
联系方式
如果想转载或者高薪挖我 请直接联系我 哈哈
wechat:
qileiwangnan
email:
qileilove@gmail.com


